Update Chrome Browser
Zyngenia Inc.’s technology is applied to create a novel class of monoclonal antibody (mAb)-based therapeutics, hereafter known as Zybody™ therapeutics. Zybodies are engineered to express multiple modular recognition domains (MRDs) that enable simultaneous binding to multiple disease targets (two to five specificities) with tunable valency (two to ten valencies). Initially, Zyngenia Inc.’s proprietary programs were built on foundations of mAb drugs within proven markets, with the goal being to enhance efficacy and widen the population of potential patients for these established mAbs. To date, Zyngenia Inc. has achieved preclinical proof-of-concept with both bi-specific and tri-specific programs in inflammation and cancer.
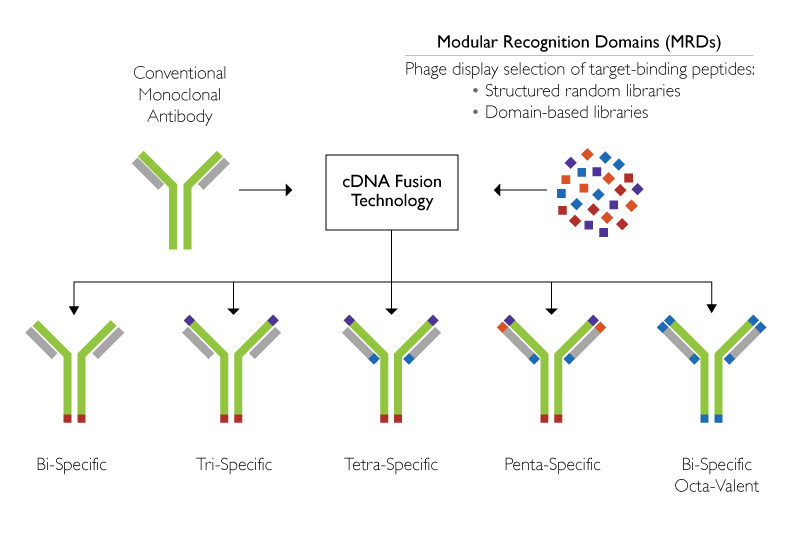

Zyngenia Inc.’s therapeutics are readily constructed from the core scaffold mAbs, to which one or more target-specific MRDs have been genetically fused.
The core scaffold mAbs used with Zyngenia Inc.’s technology can be human, humanized, or chimeric. Importantly, we make no alterations to the mAb scaffold that would change its inherent function. Thus, each Zybody maintains the essential drug-like properties of the parent mAb, including binding specificity, valency, and affinity. Additionally, the scaffold retains FcRn binding and all Fc-receptor effector functions. Zybodies are purified and produced in the same manner as traditional mAbs. They also feature CMC properties and stabilities that are comparable to mAbs that are commercially validated.
Each MRD consists of a short (typically 20-50aa) target-binding peptide that is genetically constructed to be part of the core antibody scaffold. The MRDs are easily engineered (as part of the gene) to the C or N termini of light or heavy chains of the antibodies. This “plug and play” nature allows for the rapid construction (three months) of new therapeutics using existing MRDs fused onto new scaffold antibodies. Zyngenia Inc. has designed a large number of proprietary libraries of MRDs possessing sequence diversity greater than 1010. These MRD sequences are selected to minimize potential immunogenicity and instability, both in vivo and in vitro. Additionally, selection strategies have been applied successfully to both cell surface and soluble targets.